Gum Infections Unveiled: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Introduction
Gum infections, which are also referred to as periodontal disease or periodontitis, are prevalent dental issues that impact millions of individuals across the globe. These infections vary in severity, from mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis. If left untreated, they can cause significant oral health problems, including tooth loss, so treatment of gum infection is necessory. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the different aspects of gum infections, such as their causes, symptoms, and, most significantly, the treatments that are available to combat them.
Understanding Gum Infection
What Causes Gum Infection?
The accumulation of plaque on teeth and gums is the primary cause of gum infections. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth when sugars and starches in our food interact with the bacteria in our mouths. If left unremoved through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, which is a breeding ground for more bacteria.
When bacteria invade, the body's natural response is inflammation. This causes the gums to become red and swollen, and they may bleed when brushed or flossed. The initial phase of gum disease is known as gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into a more severe condition. form of gum infection called periodontitis.
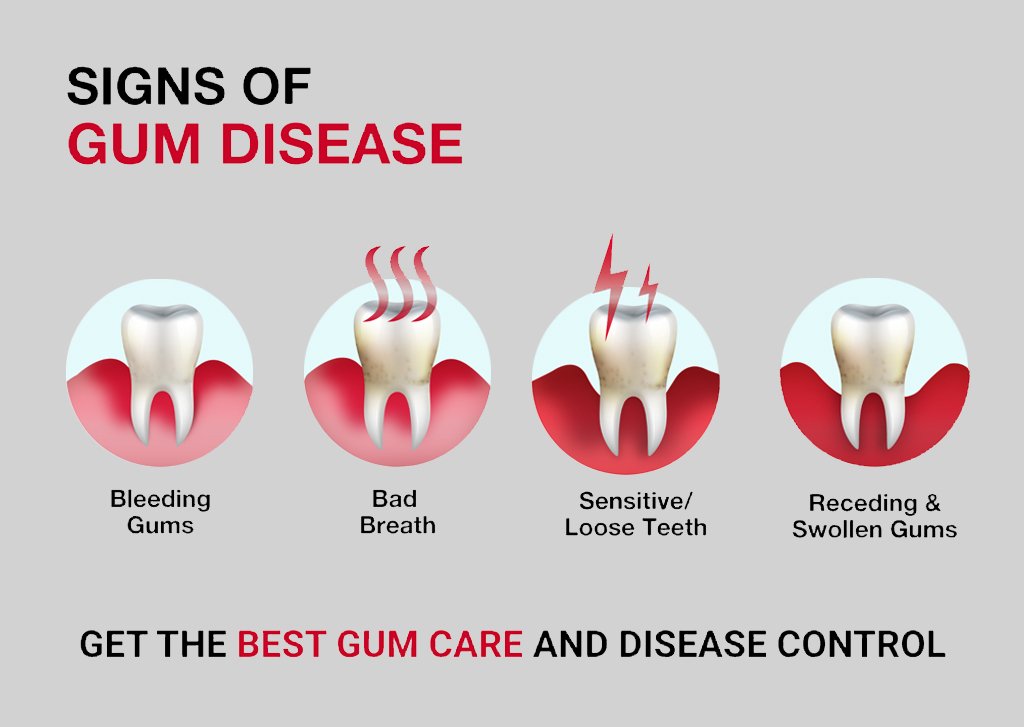
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Infection
Early intervention is crucial for gum infections. Common indications include:
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily when you brush or floss are a common early sign of gum infection.
- Swollen Gums: Inflamed or puffy gums are another telltale sign of gum disease.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath that doesn't improve with oral hygiene may be a sign of gum infection.
- Receding Gums: As gum infection progresses, the gums may start to recede, making teeth appear longer.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased tooth sensitivity, especially to hot or cold temperatures, can be a symptom of gum infection.
- Pain or Discomfort: Discomfort or pain while chewing is another symptom of advanced gum disease.
- Loose Teeth: In severe cases, gum infection can lead to tooth mobility or even tooth loss.
Treatment Options for Gum Infection
Treating gum infections is crucial to avoid oral health complications. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the infection, from at-home remedies to professional dental procedures.
- Oral Hygiene PracticesRegular Brushing and Flossing: Maintaining good oral hygiene is the first line of defense against gum infection. Brushing at least twice a day and flossing daily helps remove plaque and prevent its buildup.
- Antibacterial Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce the bacterial load in the mouth, aiding in the treatment of gum infection.
Professional Dental Cleanings
- Scaling and Root Planing: For individuals with gingivitis or early-stage periodontitis, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be recommended. During this procedure, a dentist or dental hygienist removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Routine dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and management of gum infections. Dentists can monitor your oral health and guide you on maintaining healthy gums.
Medications
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat gum infections. These can either be consumed through the mouth or applied on the skin surface.
- Antiseptic Gels: Dentists may recommend antiseptic gels or ointments that can be applied directly to the infected gums.
Surgical Procedures
- Flap Surgery: For advanced periodontitis, flap surgery may be necessary. During this procedure, the gums are lifted, and the roots are cleaned to remove tartar. The gums are then sutured back into place.
- Bone Grafting: In cases where gum infection has caused bone loss, bone grafting procedures may be performed to regenerate lost bone tissue.
- Gum Grafting: Gum grafting is done to cover exposed tooth roots caused by receding gums, improving both aesthetics and function.
Lifestyle Changes
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum infection. Successfully quitting smoking can improve the chances of successful treatment.
- Stress Management: Stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate gum infections. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can be beneficial.
Dietary Considerations
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, can support gum health.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reducing the consumption of sugary foods and drinks can help prevent plaque buildup.
Holistic and Natural Remedies
- Oil Pulling: Some people find oil pulling with coconut or sesame oil to be a natural remedy for gum infections.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel may have anti-inflammatory properties and can be applied topically to soothe gum inflammation.
- Prescription Medications
In severe cases of gum infection, prescription medications may be necessary and should only be used under the guidance of a dental professional.
Conclusion
Gum infections are a prevalent dental issue that, when ignored, can cause severe oral health problems. It is crucial to identify the signs and symptoms of gum infection and seek prompt medical attention. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and leading a healthy lifestyle can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing and managing gum infections. Remember, early detection is crucial in maintaining a healthy smile and avoiding further complications. If you suspect you have a gum infection, do not hesitate to consult with a dental specialist for individualized treatment of gum infection. Your oral health is invaluable.


.jpeg)

Comments
Post a Comment