Explore Gum Recession Therapy: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention – Your Roadmap to Oral Health.
Gum recession is a prevalent dental problem affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth begins to pull back or wear away, exposing the roots of the tooth. This can lead to various dental issues, including heightened tooth sensitivity, an increased risk of cavities, and, in severe cases, tooth loss. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, treatments, and prevention of gum recession therapy, providing you with a better understanding of this common oral health concern.
Understanding Gum Recession
To effectively address the gum recession, it is essential to first understand its causes and contributing factors. Various elements can lead to gum recession, including:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can result in the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth, leading to gum recession over time.
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing your teeth too vigorously or using a hard-bristle toothbrush can cause damage to the delicate gum tissue, contributing to recession.
- Gum Disease (Periodontitis): Untreated gum disease is a primary cause of gum recession. It can destroy the supporting bone structure and gum tissue.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum recession, as their gum tissue may naturally be thinner and more susceptible to recession.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using other tobacco products can contribute to gum recession due to the damage they cause to gum tissue and blood flow.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding or Clenching): Grinding or clenching your teeth can put excessive force on the gums, potentially leading to recession.
- Misaligned Teeth or Bite: An improper bite or teeth misalignment can result in uneven forces on the gums, leading to a recession in specific areas.
- Oral Piercings and Jewelry: Oral piercings, particularly on the lip or tongue, can rub against the gum tissue, causing irritation and potentially leading to recession.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or while using birth control, can make gum tissue more vulnerable to recession.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gum Recession
Identifying the signs and symptoms of gum recession is crucial for seeking timely treatment. Common indicators include:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures is a common early sign of gum recession.
- Longer-Looking Teeth: As the gumline recedes, more of the tooth structure becomes exposed, making the teeth appear longer.
- Visible Tooth Roots: The roots of the teeth can become exposed, often causing a yellowish appearance.
- Gaps or Spaces Between Teeth: As the gum tissue recedes, gaps or spaces may develop between the teeth.
- Tooth Mobility: Affected teeth may feel loose or less stable.
- Changes in Gumline Appearance: The gumline may appear irregular or uneven.
Gum Recession Therapy: Treatment Options
The appropriate treatment for gum recession varies based on its severity and the underlying causes. After a comprehensive examination by a dentist or periodontist, a personalized treatment plan will be developed. Here are some common gum recession therapy options:
- Scaling and Root Planing: Scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning, is often the initial treatment for gum recession caused by gum disease. This procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar from below the gumline and the smoothing of the tooth's root surfaces.
- Gum Graft Surgery: In more advanced cases of gum recession, gum graft surgery may be necessary. During this procedure, a periodontist takes a small amount of tissue from the patient's palate or another donor source and grafts it onto the affected area to cover the exposed tooth roots. This helps protect the tooth, reduce sensitivity, and enhance gum health.
- Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST): PST is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require traditional grafting. It involves making small holes in the gum tissue and repositioning the existing tissue over the exposed roots. PST typically offers a faster and less painful recovery compared to traditional grafting.
- Tissue Regeneration: In some cases, guided tissue regeneration may be used to encourage the regrowth of gum tissue and bone. This procedure involves placing a membrane between the gum tissue and the tooth's root to prevent unwanted tissue from invading the healing area.
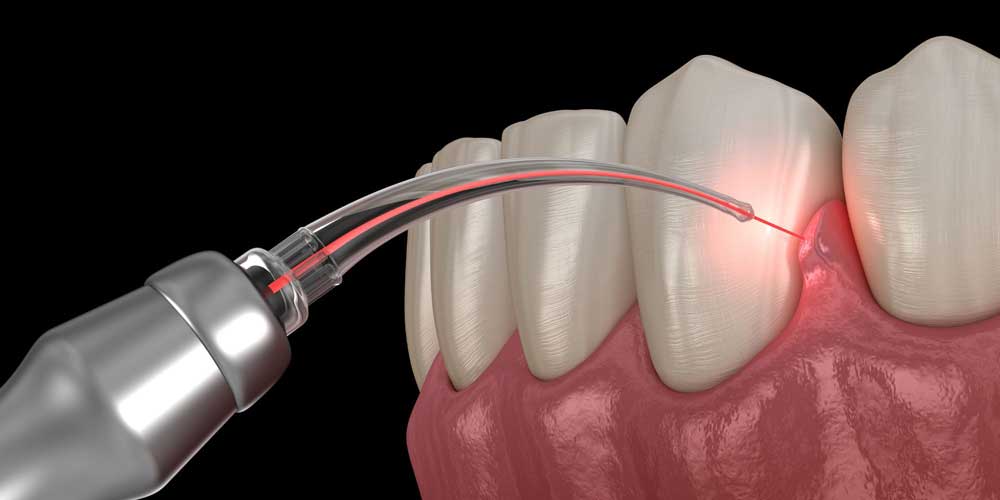
- Laser Therapy: Some dentists use lasers to treat gum recession. Laser therapy can remove damaged gum tissue and stimulate the regeneration of healthier tissue. It is less invasive and often results in less discomfort and faster healing.
Preventing Gum Recession
Prevention is always the best approach when it comes to maintaining good oral health and preventing gum recession. Here are some valuable tips to help you prevent gum recession:
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth. This routine is essential for preventing gum disease, a leading cause of gum recession.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. These appointments are crucial for early detection and treatment of gum disease, which can prevent the progression of gum recession.
- Avoid Aggressive Brushing: Use a gentle brushing technique with a soft-bristle toothbrush to avoid damaging your gums. The goal is to remove plaque and debris without causing harm.
- Manage Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): If you grind or clench your teeth, consult your dentist about a custom mouthguard. This device can protect your teeth and gums from the excessive forces generated during bruxism.
- Quit Smoking and Tobacco Use: If you are a smoker or use other tobacco products, consider quitting. Smoking can lead to gum disease and contribute to gum recession.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C, can promote gum health. Vitamin C is essential for collagen production, which is crucial for healthy gum tissue.
- Address Misaligned Teeth or Bite Issues: If you have misaligned teeth or an improper bite, consult with an orthodontist to address these issues. An orthodontic treatment plan can alleviate the uneven forces on the gums that may contribute to recession.
- Be Cautious with Oral Piercings: If you have oral piercings, be mindful of their impact on your gums. Oral piercings, especially in the lip or tongue, can rub against the gum tissue, causing irritation and potentially leading to recession. Removing or adjusting the jewelry may be necessary.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy gums and teeth is crucial, and gum recession therapy plays an essential role in achieving this. If you are experiencing any symptoms of gum recession or are concerned about your gum health, it's best to consult a dentist or periodontist for a thorough evaluation and treatment options. By following good oral hygiene practices and taking preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum recession and enjoy a lifetime of healthy smiles. Remember, early intervention is key to preserving your oral health and preventing the progression of gum recession. If you are committed to maintaining excellent oral health and preventing gum recession, you are well on your way to a lifetime of strong and healthy gums and teeth.
/assets/production/practices/7174534f3e520b204f49b7bfb36a0cb70c5a2cda/images/2469004.jpg)

.jpeg)

Comments
Post a Comment